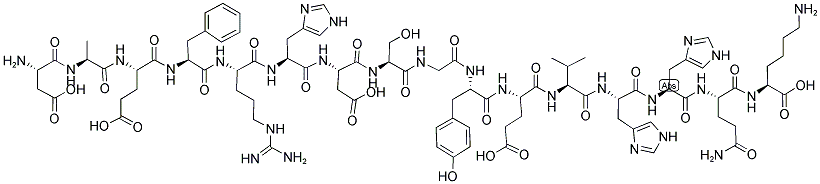
β-Amyloid (1-16) Amyloid β-Protein (1-16),99.24%
产品编号:Bellancom-P1466| CAS NO:131580-10-4| 分子式:C84H119N27O28| 分子量:1955.04
本网站销售的所有产品仅用于工业应用或者科学研究等非医疗目的,不可用于人类或动物的临床诊断或者治疗,非药用,非食用,
β-Amyloid (1-16) Amyloid β-Protein (1-16)
| 产品介绍 | β-Amyloid (1-16) 是可参与金属结合的β-淀粉样蛋白片段。 β-淀粉样蛋白是在阿尔茨海默病患者的脑中形成淀粉样斑块的肽。 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物活性 | β-Amyloid (1-16) is a β-Amyloid protein fragment involved in metal binding. Beta-amyloid is a peptide that forms amyloid plaques in the brains of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. | ||||||
| 体外研究 | |||||||
| 体内研究 |
β-amyloid (1-16) fragment is considered as valid models to examine the contribution of the key histidine residues (His , His in mouse and His , His , His in human fragments) to the Ab–Cu2+ interaction. Oxidation targets for β-Amyloid (1-16) are the histidine residues coordinated to the metal ions. Copper is bound to Aβ in senile plaque of Alzheimer’s disease with β-Amyloid (1-16) taking part in the coordination of the Cu2+ ions. Cu2+ and Zn2+ are linked with the neurotoxicity of -Amyloid and free radical damage. β-amyloid (1-16) is the minimal amino acidic sequence display a Cu coordination mode which involves three Histidines (His6, His13 and His14). β-amyloid (1-16) is supposed to be involved in metal binding. Human β-amyloid interacts with zinc ions through its metal-binding domain 1-16. The C-tails of the two polypeptide chains of the rat Aβ(1-16) dimer are oriented in opposite directions to each other, which hinders the assembly of rat Aβ dimers into oligomeric aggregates. Thus, the differences in the structure of zinc-binding sites of human and rat β-Amyloid (1-16), their ability to form regular cross-monomer bonds, and the orientation of their hydrophobic C-tails could be responsible for the resistance of rats to Alzheimer's disease. 西域 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. | ||||||
| 体内研究 |
β-amyloid (1-16) fragment is considered as valid models to examine the contribution of the key histidine residues (His , His in mouse and His , His , His in human fragments) to the Ab–Cu2+ interaction. Oxidation targets for β-Amyloid (1-16) are the histidine residues coordinated to the metal ions. Copper is bound to Aβ in senile plaque of Alzheimer’s disease with β-Amyloid (1-16) taking part in the coordination of the Cu2+ ions. Cu2+ and Zn2+ are linked with the neurotoxicity of -Amyloid and free radical damage. β-amyloid (1-16) is the minimal amino acidic sequence display a Cu coordination mode which involves three Histidines (His6, His13 and His14). β-amyloid (1-16) is supposed to be involved in metal binding. Human β-amyloid interacts with zinc ions through its metal-binding domain 1-16. The C-tails of the two polypeptide chains of the rat Aβ(1-16) dimer are oriented in opposite directions to each other, which hinders the assembly of rat Aβ dimers into oligomeric aggregates. Thus, the differences in the structure of zinc-binding sites of human and rat β-Amyloid (1-16), their ability to form regular cross-monomer bonds, and the orientation of their hydrophobic C-tails could be responsible for the resistance of rats to Alzheimer's disease. 西域 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. | ||||||
| 性状 | Solid | ||||||
| 溶解性数据 | |||||||
| 运输条件 | Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. | ||||||
| 储存方式 |
Sealed storage, away from moisture
*该产品在溶液状态不稳定,建议您现用现配,即刻使用。 | ||||||
| 参考文献 |
|

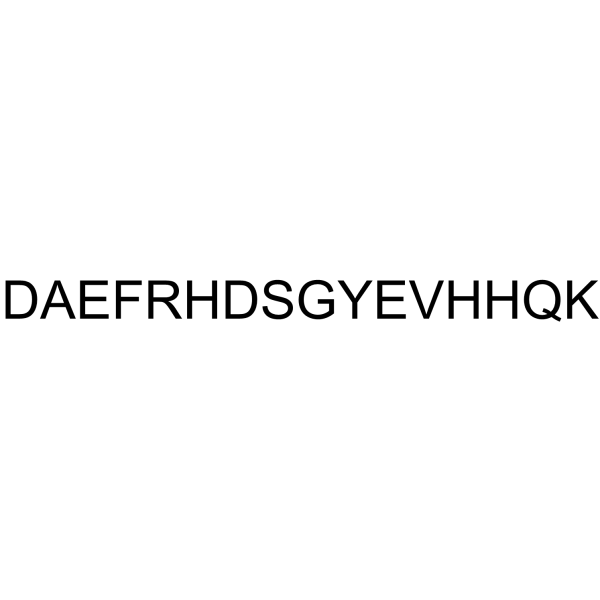





 浙公网安备 33010802013016号
浙公网安备 33010802013016号